Understanding the Causes of Hair Loss
Genetic Factors
One of the most prevalent causes of hair loss is genetics. Conditions like androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, are inherited. In men, it typically leads to a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while in women, it may result in a general thinning all over the scalp. The genes involved affect the sensitivity of hair follicles to hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which gradually shrinks the follicles over time, leading to thinner and shorter hair strands until they eventually stop growing.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalances can play a significant role in hair loss. For example, during pregnancy, hormonal changes can cause temporary hair thickening due to increased estrogen levels. However, after childbirth, when hormones return to normal, many women experience significant hair loss as the body adjusts. In men, an increase in DHT, which is a derivative of testosterone, can bind to hair follicle receptors and cause them to miniaturize, resulting in androgenetic alopecia. Other hormonal disorders such as thyroid problems (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism) can also lead to hair loss by disrupting the normal growth cycle of the hair.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients is another factor that can contribute to hair loss. Proteins, iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamins A, C, D, and E are all crucial for healthy hair growth. If the body does not receive an adequate supply of these nutrients, it can affect the hair growth cycle. For instance, iron deficiency anemia is a common cause of hair loss, as iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen to the hair follicles. Similarly, a deficiency in biotin can lead to brittle hair and hair loss.
Medical Conditions and Treatments
Certain medical conditions such as alopecia areata (an autoimmune condition that attacks the hair follicles), scalp infections (like fungal infections), and systemic diseases (such as lupus or diabetes) can cause hair loss. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy often result in hair loss as they target rapidly dividing cells, including those in the hair follicles. These types of hair loss are usually more severe and may require different approaches to treatment compared to genetic or hormonal hair loss.
Stress
Chronic stress can also have a negative impact on hair growth. It can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle by causing a condition called telogen effluvium. In this case, more hair than usual enters the resting phase (telogen) and then falls out several months later. Stress can be due to various factors such as work pressure, relationship problems, or major life changes.
Types of Medications for Hair Loss
Minoxidil
Mechanism of Action: Minoxidil is a topical medication that is available over the counter in various strengths (e.g., 2% for women and 5% or higher for men). It works by widening blood vessels in the scalp, which improves blood flow to the hair follicles. This increased blood supply delivers more nutrients and oxygen to the follicles, promoting hair growth. It also extends the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle, allowing the hair to grow for a longer period before entering the resting phase.
Effectiveness: Studies have shown that minoxidil can be effective in slowing down hair loss and promoting some regrowth. However, the results can vary from person to person. Some individuals may see significant improvement in hair density and thickness, while others may have more modest results. It usually takes several months of continuous use to see noticeable changes, and the hair growth may not be permanent. Once the medication is stopped, the hair may gradually return to its pre-treatment state.
Side Effects: Minoxidil is generally well-tolerated, but some people may experience side effects such as scalp irritation, itching, redness, and dryness. In rare cases, it can cause unwanted hair growth on other parts of the body where the solution is accidentally applied.
Finasteride
Mechanism of Action: Finasteride is an oral medication that is primarily used for male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. By reducing the levels of DHT in the body, finasteride helps to prevent the shrinking of hair follicles that is caused by DHT. This allows the hair follicles to remain in the growth phase longer and can lead to improved hair growth.
Effectiveness: Clinical trials have demonstrated that finasteride can be effective in reducing hair loss and increasing hair count in many men. It typically shows better results in younger men who have recently started experiencing hair loss.
However, like minoxidil, the effects are not always permanent, and the medication needs to be taken continuously for maintained results.
Side Effects: Finasteride may have some potential side effects, including sexual dysfunction such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation problems. These side effects are relatively rare but can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is important for men considering taking finasteride to discuss these potential risks with their healthcare provider.
Spironolactone (for Women)
Mechanism of Action: Spironolactone is a medication that is sometimes used to treat female pattern hair loss. It works by blocking the effects of androgens (male hormones) in the body. Although women also produce small amounts of androgens, an excess can contribute to hair loss. By reducing the activity of these hormones, spironolactone can help to slow down hair loss and may promote some regrowth. It also has a diuretic effect, which can help to reduce fluid retention in some cases.
Effectiveness: Studies have shown that spironolactone can be beneficial for some women with hormonal hair loss. It may take several months to see significant results, and the improvement in hair growth may vary. It is often used in combination with other treatments such as topical minoxidil for better outcomes.
Side Effects: Possible side effects of spironolactone include menstrual irregularities, breast tenderness, and electrolyte imbalances. It is important to have regular check-ups while taking this medication to monitor for any potential side effects and to ensure that the body’s electrolyte levels remain normal.
Biotin Supplements
Mechanism of Action: Biotin is a B vitamin that is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids and plays a role in maintaining the health of the skin, nails, and hair. Biotin supplements are thought to help with hair loss by providing the necessary nutrients for healthy hair growth. It may improve the strength and elasticity of the hair shaft and support the overall health of the hair follicles.
Effectiveness: While biotin deficiency can cause hair loss, the effectiveness of biotin supplements in treating hair loss in individuals with normal biotin levels is less clear. Some studies have shown a modest improvement in hair growth and quality with biotin supplementation, but more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Side Effects: Biotin supplements are generally considered safe when taken in the recommended doses. However, taking very high doses (much higher than the recommended daily intake) may cause side effects such as skin rashes, digestive issues, and interference with certain laboratory tests.
Other Medical Approaches to Treating Hair Loss
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
How It Works: LLLT devices use low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes to stimulate the hair follicles. The light energy is absorbed by the cells in the follicles, which triggers a series of biochemical reactions that can promote hair growth. It is thought to increase cell metabolism, improve blood circulation, and reduce inflammation in the scalp.
Effectiveness: Some studies have shown that LLLT can be effective in reducing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth. It is often used as an adjunct therapy along with medications like minoxidil. However, the results may vary depending on the individual and the severity of the hair loss. LLLT devices are available in the form of helmets, combs, or handheld devices, and they require regular use over a period of several months to see noticeable results.
Safety: LLLT is generally considered safe and does not cause significant side effects. However, it is important to use FDA-approved devices and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Some people may experience mild scalp warmth or a tingling sensation during treatment, but these are usually not harmful.
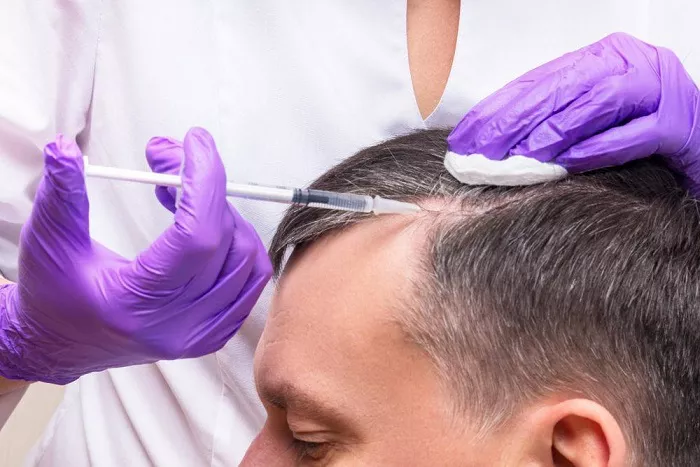
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Procedure: PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate cell proliferation and tissue regeneration. By injecting PRP into the scalp, it is hoped that these growth factors will promote hair growth and improve the health of the hair follicles.
Effectiveness: There is some evidence to suggest that PRP therapy can be effective in treating hair loss, especially in cases of androgenetic alopecia. However, more research is needed to establish its long-term effectiveness and optimal treatment protocols. Some patients may see an improvement in hair density and thickness after a series of PRP injections, but the results can vary.
Considerations: PRP therapy is a relatively new and evolving treatment. It requires multiple sessions, usually spaced a few weeks apart, and can be costly. There may also be some mild discomfort during the injection process, and there is a small risk of infection or other complications at the injection site.
The Importance of Early Intervention and a Comprehensive Approach
Early Intervention
The earlier hair loss is addressed, the better the chances of successful treatment. When hair loss first begins, the hair follicles may still have some viability, and medications or other treatments may be more effective in preventing further damage and promoting regrowth. If left untreated for a long time, the hair follicles may become irreversibly damaged, making it more difficult to achieve significant improvement.
It is important to identify any potential underlying causes of hair loss early on. For example, if a hormonal imbalance is detected and treated promptly, it may be possible to stop or slow down the hair loss and even reverse it to some extent. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help in detecting any early signs of hair loss and initiating appropriate treatment.
Comprehensive Approach
Treating hair loss often requires a comprehensive approach that includes not only medications but also lifestyle changes and proper hair care. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in essential nutrients, reducing stress levels, avoiding harsh hair treatments and styling practices, and keeping the scalp clean and healthy are all important factors.
For example, a balanced diet that includes proteins, vitamins, and minerals can provide the necessary building blocks for healthy hair growth. Stress management techniques such as meditation and exercise can help to reduce the impact of stress on the hair growth cycle. Using gentle shampoos and conditioners and avoiding tight hairstyles that can pull on the hair can also prevent further damage.
In some cases, a combination of different medications or treatments may be more effective than using a single approach. For instance, combining minoxidil with finasteride or using PRP therapy along with topical medications may provide better results for some individuals. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate comprehensive treatment plan based on the individual’s specific situation and needs.
Conclusion
Related Topics: