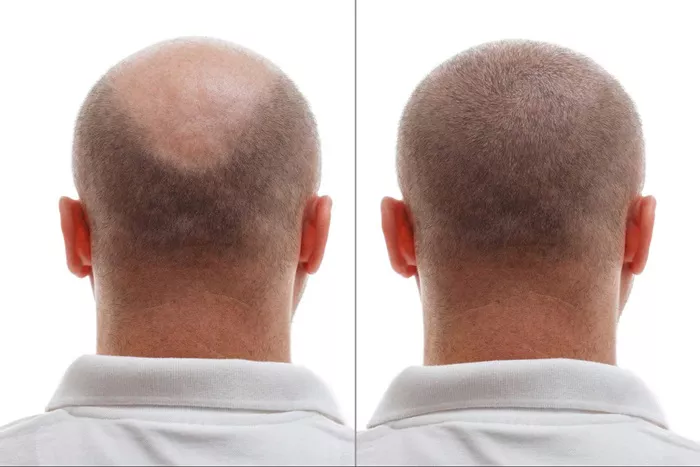
Hair transplants have become increasingly popular as a solution for those suffering from hair loss. However, a question that often arises is: Can hair transplants cause baldness? This is a concern for many considering the procedure, and it’s essential to understand the risks and outcomes associated with hair transplantation.
Understanding Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to the balding or thinning areas. There are two main methods of hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
FUT:
Involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area and then dissecting it into individual follicular units to be transplanted.
FUE:
Involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area and then implanting them into the recipient area.
Both techniques are widely used, and each has its advantages and disadvantages.
How Hair Transplants Work
The fundamental principle of hair transplantation is to redistribute hair from areas that are resistant to balding (typically the back and sides of the scalp) to areas where hair loss is prominent. This is because the hair in these donor areas is usually not affected by the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is responsible for male pattern baldness.
Does Hair Transplantation Cause Baldness?
The idea that hair transplants can cause baldness is a myth. However, several factors can lead to the perception that a hair transplant has caused further hair loss or balding. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone considering a hair transplant.
Shock Loss: A Temporary Phenomenon
One of the most common concerns after a hair transplant is shock loss. Shock loss refers to the temporary shedding of hair that can occur in both the donor and recipient areas after the procedure. This shedding happens because the trauma of the surgery can temporarily disrupt the normal hair growth cycle.
Shock Loss in the Donor Area:
In the donor area, shock loss can occur due to the extraction or removal of hair follicles. This loss is usually temporary, and the hair typically regrows within a few months.
Shock Loss in the Recipient Area:
In the recipient area, the implanted hair follicles can go into a resting phase before they start growing again. This can cause a temporary appearance of increased baldness, but it’s important to understand that this is part of the normal healing process.
Permanent Hair Loss and Hair Transplantation
While shock loss is temporary, some factors can lead to permanent hair loss after a hair transplant. These factors are usually related to the patient’s existing condition and the quality of the surgical procedure.
Progressive Hair Loss:
Hair transplantation does not stop the progression of genetic hair loss. If a patient continues to lose hair in areas that were not treated, it may give the impression that the transplant has caused further balding. Therefore, it’s essential to have a long-term plan and possibly consider future transplants to address ongoing hair loss.
Poor Surgical Technique:
In rare cases, poor surgical technique can damage the hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss. This is why it’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon to perform the procedure.
The Role of DHT in Hair Loss
DHT, or dihydrotestosterone, plays a significant role in male pattern baldness. DHT binds to receptors in the hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair. The hair follicles used in transplants are typically resistant to DHT, but the surrounding native hair may still be susceptible to DHT, leading to ongoing hair loss in untreated areas.
Pre-existing Conditions and Hair Transplantation
Certain pre-existing conditions can affect the outcome of a hair transplant and contribute to the appearance of baldness after the procedure.
Alopecia Areata:
This is an autoimmune condition that causes patches of hair loss. It can occur even after a successful hair transplant and may give the impression that the transplant has caused baldness.
Scalp Conditions:
Conditions like scalp psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis can affect the health of the scalp and hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
The Importance of Post-Transplant Care
Proper post-operative care is crucial to the success of a hair transplant. Failure to follow the surgeon’s instructions can lead to complications, including infection, which can damage the hair follicles and result in hair loss.
Avoiding Physical Trauma:
The transplanted area is sensitive after surgery, and physical trauma, such as scratching or rubbing, can damage the follicles and cause hair loss.
Using Prescribed Medications:
Following the prescribed medication regimen, including antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can help prevent infection and promote healing.
SEE ALSO: How to Wash Your Head After a Hair Transplant?
Hair Transplantation and Scarring
Scarring is another factor that can contribute to the appearance of hair loss after a transplant. Both FUT and FUE techniques can leave scars, though they are usually minimal and well-hidden by the surrounding hair.
FUT Scarring:
FUT can leave a linear scar in the donor area, which can be noticeable if the hair is cut very short.
FUE Scarring:
FUE leaves tiny dot scars that are less noticeable, but if too many follicles are extracted from a small area, it can lead to a thinning appearance.
Patient Expectations and Psychological Factors
Patient expectations play a significant role in satisfaction with hair transplant results. Unrealistic expectations can lead to disappointment and the perception that the transplant has caused further balding.
Understanding the Limitations:
Hair transplantation can improve hair density, but it cannot restore the original thickness or quantity of hair.
Psychological Impact:
The stress of undergoing surgery and the recovery process can contribute to hair shedding, as stress is a known factor in hair loss.
Preventing Further Hair Loss After Transplantation
To prevent further hair loss after a transplant, patients can take several proactive steps:
Medications:
Medications like finasteride and minoxidil can help slow down the progression of hair loss and protect the remaining hair.
Lifestyle Changes:
Reducing stress, improving diet, and avoiding smoking can help maintain the health of the hair and scalp.
Regular Follow-Ups:
Regular follow-ups with the surgeon can help monitor the condition of the hair and scalp and address any issues early.
Conclusion
Hair transplantation is a highly effective solution for hair loss, but it is not without its risks and limitations. While hair transplants do not cause baldness, several factors can contribute to the perception of increased hair loss after the procedure. Understanding these factors and managing expectations is crucial for anyone considering hair transplantation. By choosing a skilled surgeon, following post-operative care instructions, and taking steps to protect the remaining hair, patients can achieve satisfying and long-lasting results.