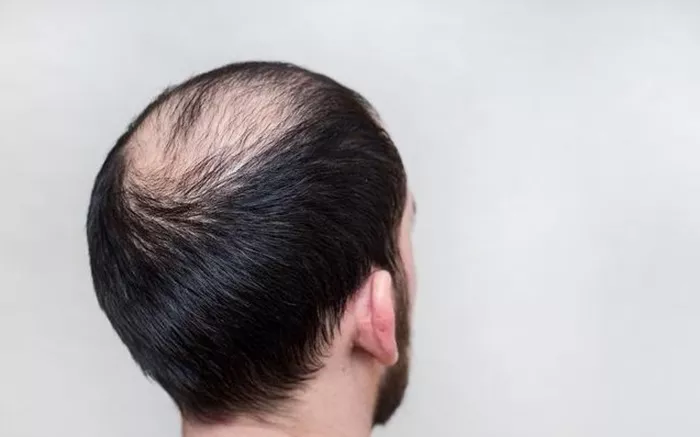
Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition affecting both men and women. Understanding when it begins and the factors influencing its onset is crucial for early intervention and management. This article provides a comprehensive look at the timeline of hereditary hair loss, its triggers, and how it can be managed effectively.
Understanding Hereditary Hair Loss
Hereditary hair loss is a genetic condition that can lead to gradual thinning of the hair and eventual hair loss. It is the most common form of hair loss and can affect individuals of all ages.
Age of Onset
The onset of hereditary hair loss varies greatly among individuals. For men, it typically begins in their late teens to early twenties. Women may start to experience thinning hair in their late twenties to early thirties. However, the condition can begin earlier or later depending on genetic predisposition.
Genetic Factors
Hereditary hair loss is influenced by genetics. The condition is linked to genes inherited from both parents, although the exact mechanism is complex. It is not solely determined by one gene but rather a combination of multiple genes that contribute to the likelihood of developing the condition.
Early Signs and Symptoms
The initial signs of hereditary hair loss may include a gradual thinning of the hair on the top of the head, a receding hairline, or increased hair shedding. These symptoms can be subtle at first but become more noticeable over time.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of hereditary hair loss typically involves a medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes a scalp biopsy. In some cases, genetic testing may be used to confirm the condition, though it is not always necessary.
Impact of Hormones
Hormones play a significant role in hereditary hair loss. The condition is associated with androgens, which are male hormones present in both men and women. These hormones affect the hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and loss.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for managing hereditary hair loss. These include:
Medications:
Drugs such as minoxidil and finasteride can help slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth. Minoxidil is available over the counter, while finasteride requires a prescription.
SEE ALSO: Is Hair Loss a Sign of Ovarian Cancer?
Hair Transplant Surgery:
This procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from one part of the scalp to another. It is a more permanent solution but requires careful consideration and consultation with a specialist.
Lifestyle Changes:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and stress management, can help support hair health and potentially slow the progression of hair loss.
Topical Treatments:
Products containing ingredients like ketoconazole or corticosteroids can be applied to the scalp to reduce inflammation and improve hair growth.
Prevention Strategies
While hereditary hair loss cannot be completely prevented, early intervention can help manage and slow its progression. Regular monitoring of hair health and seeking professional advice at the first signs of thinning can be beneficial.
Psychological Impact
The psychological impact of hereditary hair loss can be significant. It can affect self-esteem and confidence, leading to emotional distress. Support from mental health professionals, support groups, and counseling can be helpful in coping with these challenges.
Future Research
Ongoing research is exploring new treatments and potential cures for hereditary hair loss. Advances in genetic research and regenerative medicine hold promise for more effective interventions in the future.
Conclusion
Hereditary hair loss is a complex condition with a varied timeline of onset and progression. Understanding the factors that contribute to its development and the available treatment options can help individuals manage the condition effectively. Early intervention and support are key to maintaining hair health and overall well-being.
This comprehensive overview provides insights into when hereditary hair loss starts, its underlying causes, and the available options for managing the condition. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can navigate the challenges of hereditary hair loss with greater confidence and control.
FAQs
How Do You Know If You Have Hereditary Hair Loss?
Hereditary hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, is typically identified through a combination of clinical examination, family history, and sometimes diagnostic tests. Here’s how you can determine if you have this condition:
Family History: Hereditary hair loss often runs in families. If your parents, grandparents, or siblings have experienced similar symptoms, it increases the likelihood that your hair loss may be hereditary.
Pattern of Hair Loss:
Men: The most common pattern is a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, eventually leading to bald spots. In some cases, hair loss can progress to complete baldness on the top of the head.
Women: Women usually experience diffuse thinning over the top of the head rather than a receding hairline. The hair thinning is often less noticeable than in men.
Age of Onset: Hereditary hair loss often begins in late teens to early twenties for men and late twenties to early thirties for women. However, it can start earlier or later depending on individual genetics.
Medical Evaluation:
Scalp Examination: A dermatologist will examine your scalp to assess the pattern of hair loss and the condition of the hair follicles.
Biopsy: In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be performed to examine the hair follicles under a microscope and confirm the diagnosis.
Genetic Testing: While not commonly used, genetic testing can sometimes be employed to identify specific markers associated with hereditary hair loss.
Hair Loss Progression: The gradual nature of hair thinning over time is a common feature of hereditary hair loss. Sudden or patchy hair loss may indicate other conditions, such as alopecia areata.
Can You Prevent Hereditary Hair Loss?
While you cannot prevent hereditary hair loss entirely due to its genetic nature, there are strategies to manage and potentially slow down the progression:
Early Intervention: The earlier you start treatment, the more effective it may be in slowing down hair loss and promoting hair regrowth. Medications like minoxidil and finasteride can be beneficial when used early.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall hair health. Regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep also play important roles in maintaining hair quality.
Avoiding Damage: Minimize damage to your hair by avoiding excessive heat styling, harsh chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles that can pull on the hair.
Topical Treatments: Products designed to improve scalp health and strengthen hair follicles can help manage hair thinning. Ingredients like ketoconazole and biotin are commonly used in topical treatments.
Hair Care Products: Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to avoid stripping the hair of natural oils and to reduce scalp irritation.
How Long Does It Take to Get Genetic Baldness?
The timeline for developing genetic baldness varies significantly from person to person:
Men: Hair loss typically starts in the late teens to early twenties and can progress to baldness over several years to decades. The rate of progression depends on genetic factors and individual response to treatment.
Women: Women usually experience a slower progression of hair thinning, with the process starting in their late twenties to early thirties. The rate at which hair loss progresses can vary, with some women experiencing gradual thinning over many years.
Onset and Progression: In both men and women, the process is gradual. It can take several years for significant hair loss to become noticeable. Early signs such as thinning or a receding hairline may appear before more severe baldness develops.
At What Age Do You Start Losing a Lot of Hair?
The age at which you start losing a significant amount of hair depends on several factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and overall health:
Men: Most men begin to notice hair loss in their late teens to early twenties. Significant hair loss or baldness may become more apparent in the late twenties to early thirties.
Women: Women typically start experiencing noticeable hair thinning in their late twenties to early thirties. Significant hair loss tends to progress more slowly compared to men.
Individual Variation: Hair loss patterns and severity can vary widely. Some individuals may experience noticeable hair loss earlier or later than the typical age ranges mentioned.