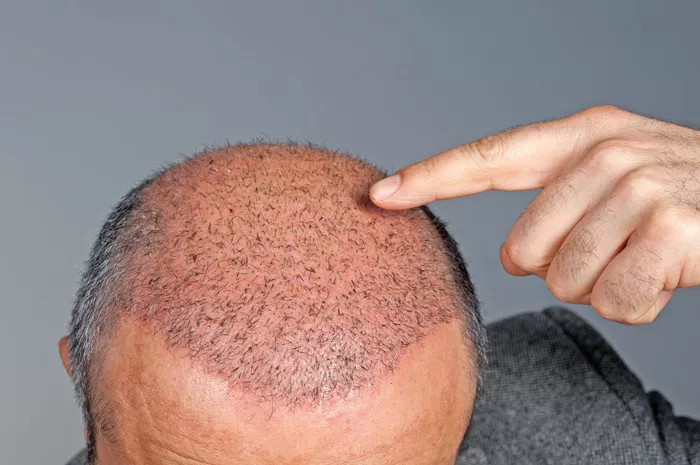
Androgenetic alopecia is a common form of hair loss. It affects both men and women. In men, it is often called male pattern baldness. In women, it is known as female pattern hair loss. This condition is largely genetic. Hormones, specifically androgens, play a significant role. Hair follicles shrink over time. This results in thinner hair and eventually, hair loss.
The Impact of Androgenetic Alopecia
Hair loss can be distressing. It affects self-esteem and confidence. Many people seek treatments to restore their hair. Options include medications, lifestyle changes, and surgical procedures. Among the surgical options, hair transplants are popular.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure. It involves moving hair from one part of the body to another. The goal is to cover areas with thinning or no hair. There are two main types of hair transplant techniques: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT is also known as strip surgery. A strip of scalp with healthy hair is removed. The strip is usually taken from the back of the head. The area is then stitched closed. The strip is divided into tiny grafts. Each graft contains one or more hair follicles. These grafts are implanted into the thinning or balding areas.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more modern technique. Individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area. No strip of scalp is removed. This method leaves tiny, round scars. These scars are less noticeable than the linear scar from FUT. The extracted follicles are then implanted into the balding areas.
Suitability for Androgenetic Alopecia
Hair transplants can be effective for androgenetic alopecia. However, not everyone is a suitable candidate. Factors to consider include the extent of hair loss, the quality of the donor hair, and the overall health of the individual.
Evaluating Hair Loss Extent
A thorough assessment is crucial. Dermatologists or hair transplant surgeons evaluate the pattern and extent of hair loss. Early stages of androgenetic alopecia might not require surgery. In advanced stages, sufficient donor hair is needed.
Quality of Donor Hair
The quality of donor hair is vital. Hair from the back and sides of the head is typically more resistant to androgenetic alopecia. This makes it ideal for transplantation. Thin or weak donor hair may not yield satisfactory results.
Health Considerations
Overall health affects the success of a hair transplant. Conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or autoimmune disorders can impact healing. A detailed medical history is essential before proceeding.
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
Consultation and Planning
The process begins with a consultation. The surgeon assesses the hair loss and discusses expectations. A personalized treatment plan is created. This includes deciding the number of grafts needed and the technique to be used.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Certain preparations are necessary before surgery. Patients may need to avoid specific medications. Smoking and alcohol consumption should be minimized. Instructions for washing hair and scalp care are provided.
The Surgery Day
On the day of surgery, the patient arrives at the clinic. Local anesthesia is administered to numb the scalp. The donor area is prepared, and the hair follicles are harvested. This can take several hours, depending on the number of grafts needed.
Implantation of Hair Follicles
The harvested follicles are carefully implanted into the recipient area. Tiny incisions are made in the scalp. The surgeon places each graft individually. Precision is crucial for a natural-looking result.
Post-Surgery Care
After the procedure, specific aftercare is necessary. The patient receives instructions on how to care for the transplanted area. Medications for pain and infection prevention might be prescribed. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor progress.
SEE ALSO: Can Hair Transplant Thicken Hair?
Results and Expectations
Hair transplant results vary. Initial shedding of transplanted hair is normal. New hair growth typically starts after a few months. Full results can take up to a year.
Natural-Looking Hair
The goal is a natural-looking result. Skilled surgeons place grafts to mimic natural hair growth patterns. This ensures that the hair blends seamlessly with existing hair.
Longevity of Results
Hair transplants for androgenetic alopecia are generally long-lasting. The transplanted hair is resistant to the hormonal effects that cause hair loss. However, ongoing hair loss in non-transplanted areas can occur. Some patients may require additional sessions in the future.
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks. Potential complications include infection, scarring, and graft failure. Choosing an experienced surgeon minimizes these risks.
Infection
Proper hygiene and care reduce infection risks. Patients should follow post-surgery instructions meticulously.
Scarring
FUT leaves a linear scar. FUE leaves tiny round scars. The choice of technique can influence the visibility of scars.
Graft Failure
Not all grafts may take root. Some might not grow as expected. This can affect the overall result.
Cost Considerations
Hair transplant costs vary widely. Factors influencing cost include the number of grafts, the technique used, and the surgeon’s expertise. In some regions, hair transplants can be very expensive.
Insurance and Financing
Most insurance plans do not cover hair transplants. This is because they are considered cosmetic procedures. Some clinics offer financing options to make the procedure more affordable.
Alternatives to Hair Transplant
Hair transplants are not the only option for treating androgenetic alopecia. Alternatives include medications like minoxidil and finasteride, low-level laser therapy, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments.
Medications
Minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved treatments. They can slow hair loss and promote regrowth. However, they require ongoing use to maintain results.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT involves using lasers to stimulate hair growth. It is a non-invasive treatment. Results can vary among individuals.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
PRP treatment involves injecting a concentration of a patient’s own platelets into the scalp. This can stimulate hair growth. Multiple sessions are often needed for optimal results.
Conclusion
Hair transplants can be an effective solution for androgenetic alopecia. They offer a long-term and natural-looking solution. However, they are not suitable for everyone. A thorough evaluation and consultation with a skilled surgeon are essential. Understanding the procedure, costs, and potential risks is crucial for making an informed decision. While hair transplants can restore confidence and improve appearance, it is important to have realistic expectations and follow post-surgery care instructions carefully.