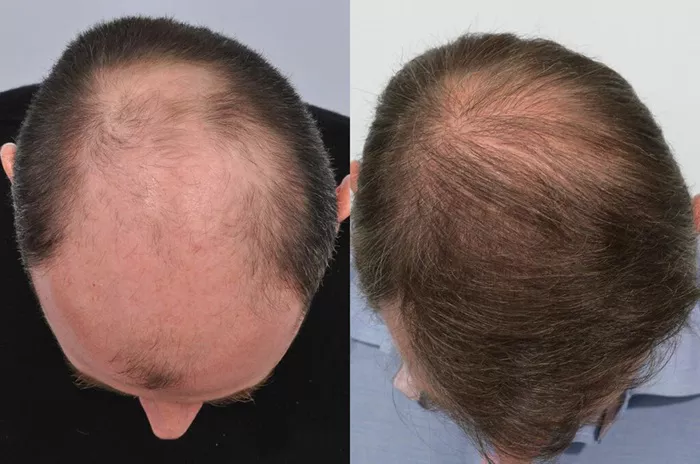
Hair transplantation is a significant decision for individuals seeking to restore their hair density and improve their appearance. However, some patients may notice that their hair remains thin even after the procedure. Understanding why this happens requires delving into several factors that influence hair growth post-transplantation.
Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). During a hair transplant, hair follicles are typically harvested from areas of dense growth (donor site) and implanted into areas with thinning or balding hair (recipient site). Despite the meticulous process, the initial growth after transplantation can vary among individuals.
Factors Influencing Hair Density Post-Transplant
Genetics:
Genetic predisposition plays a crucial role in determining hair characteristics, including thickness and growth patterns. While hair transplantation relocates hair follicles, the inherent genetic programming of these follicles can affect their growth rate and eventual density.
Post-Operative Care:
Proper post-operative care is vital for optimal hair growth after transplantation. This includes following the surgeon’s instructions regarding washing, moisturizing, and avoiding activities that may disrupt the healing process. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can impact the survival and growth of transplanted hair follicles.
Shock Loss:
Immediately following hair transplantation, some patients experience “shock loss,” where the native hairs in the recipient area may temporarily fall out. This is a natural response to the trauma of surgery and typically resolves within a few weeks to months as new hair growth begins.
Follicle Survival Rate:
The survival rate of transplanted hair follicles varies depending on several factors, including the harvesting technique, the skill of the surgeon, and the quality of the recipient site tissue. Higher survival rates generally lead to better hair density outcomes post-transplantation.
SEE ALSO: How Long to Take Medicine After Hair Transplant?
Underlying Scalp Conditions:
Pre-existing scalp conditions such as dermatitis or psoriasis can affect the success of hair transplantation. These conditions may interfere with the healing process and compromise the growth of transplanted hair follicles.
Hair Characteristics:
The natural thickness and texture of hair follicles play a role in the perceived density post-transplantation. Fine or thin hair follicles may not provide the same coverage or density as thicker follicles, even after successful transplantation.
Patient Expectations:
Managing patient expectations is crucial in hair transplantation. While modern techniques aim to achieve natural-looking results, individual variations in hair growth patterns and the need for multiple sessions may influence the final density achieved.
Addressing Thin Hair Post-Transplantation
Consultation and Evaluation:
If you’re concerned about thinning hair after a transplant, schedule a follow-up consultation with your surgeon. They can evaluate the progress of your hair growth and determine if additional treatments or adjustments are necessary.
Medical Treatments:
In some cases, supplementary medical treatments such as minoxidil (Rogaine) or finasteride (Propecia) may be prescribed to enhance hair growth and density post-transplantation. These medications can help stimulate hair follicles and improve overall coverage.
Revision or Touch-Up Procedures:
Depending on your individual response to the initial transplant, your surgeon may recommend a revision or touch-up procedure to increase hair density in specific areas. This is typically considered once the initial transplanted hairs have fully grown and stabilized.
Patience and Time:
Hair transplantation is a gradual process, and final results may not be fully evident until 12-18 months after the procedure. Patience is essential as transplanted hairs go through their growth cycles and mature into thicker, fuller strands.
Conclusion
While hair transplantation offers a promising solution for restoring hair density, it’s essential to recognize that achieving optimal results takes time and careful management. Factors such as genetics, post-operative care, and the natural growth cycle of hair follicles all contribute to the final outcome. By understanding these factors and working closely with your surgeon, you can navigate the journey to thicker, more natural-looking hair post-transplantation.
In conclusion, thinning hair after a transplant can stem from various factors, but with proper care and realistic expectations, patients can achieve satisfying results over time. For anyone considering or recovering from hair transplantation, consulting with a qualified surgeon and following their guidance is key to maximizing the success of the procedure.
FAQs
Will my transplanted hair get thicker?
Yes, typically transplanted hair will undergo a maturation process over time. Initially, the hair may appear fine or sparse, but as the hair follicles settle into their new location and begin to grow, the hair shafts often thicken. This process can take several months, with final results becoming more apparent around 12-18 months post-transplantation.
Why is my hair not growing after a hair transplant?
After a hair transplant, it’s common for patients to experience a temporary shedding phase known as “shock loss.” This occurs due to the trauma of surgery and can lead to the temporary cessation of hair growth in the transplanted follicles. However, this is usually followed by a period of regrowth as the follicles enter the anagen (growth) phase again. If hair growth seems stalled or minimal, it’s essential to consult your surgeon to rule out any complications or discuss potential treatments.
Is a hair transplant still thin at 7 months?
At 7 months post-transplantation, it’s normal for transplanted hair to still be in the early stages of growth and maturation. While some patients may notice significant improvement in hair density by this time, others may still perceive thinning or sparse areas. It’s important to remember that hair growth post-transplantation is gradual, and final results may continue to improve up to 12-18 months after the procedure. If concerns about thinning persist, consulting your surgeon for a follow-up evaluation is recommended to assess progress and discuss potential next steps.
You May Be Interested In