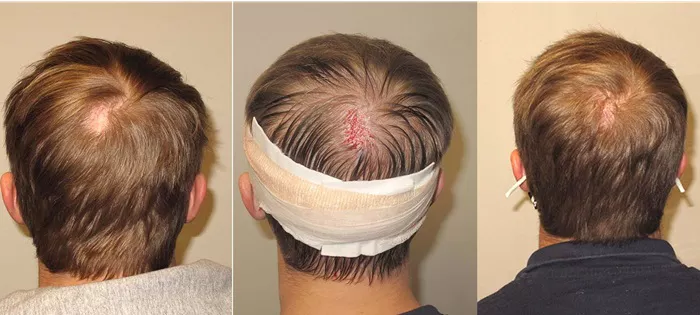
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure. It involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body to another. Typically, hair is taken from the back or sides of the head. This area is known as the donor site. The hair is then transplanted to the balding or thinning areas. This area is known as the recipient site. The goal is to achieve natural-looking hair growth in the recipient area.
There are two main types of hair transplant procedures. They are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT involves removing a strip of skin with hair follicles from the donor site. The follicles are then individually transplanted to the recipient site. FUE, on the other hand, involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor site. These follicles are then transplanted to the recipient site.
Anesthesia and Pain Management
Anesthesia Used During Hair Transplants
Both FUT and FUE procedures require anesthesia. Local anesthesia is commonly used. This means the patient is awake during the procedure. However, the area being worked on is numbed. This helps to minimize pain and discomfort. The anesthesia is usually administered through injections. These injections may cause slight discomfort. However, once the anesthesia takes effect, the patient should not feel pain in the treated areas.
Some patients may also be given oral sedatives. This helps them to relax during the procedure. In rare cases, general anesthesia may be used. This means the patient is completely unconscious during the procedure. General anesthesia is typically reserved for more extensive procedures.
Managing Pain During the Procedure
The use of local anesthesia ensures that the procedure itself is not painful. Patients may feel some pressure or movement. However, they should not feel pain in the numbed areas. The discomfort from the initial injections is usually brief. Once the anesthesia takes effect, the patient should be comfortable.
Some patients may experience anxiety about the procedure. In such cases, the surgeon may offer additional measures to ensure comfort. This can include offering oral sedatives or using calming techniques.
Pain and Discomfort After the Procedure
Immediate Post-Operative Pain
After the procedure, the effects of the anesthesia will wear off. Patients may start to feel some discomfort or pain. This is a normal part of the healing process. The level of pain varies from person to person. It also depends on the type of procedure performed.
FUT procedures may result in more immediate post-operative pain. This is because the procedure involves a larger incision. Patients may experience pain at the donor site. They may also feel tightness or discomfort in the scalp. Pain medication is typically prescribed to manage this discomfort.
FUE procedures generally result in less immediate post-operative pain. This is because the procedure involves smaller, individual extractions. However, patients may still experience some discomfort or soreness. Pain medication is also prescribed for these patients.
Long-Term Pain and Discomfort
Most patients do not experience long-term pain after a hair transplant. However, some may experience temporary discomfort as the scalp heals. This can include itching, tightness, or a tingling sensation. These symptoms typically subside within a few weeks.
In rare cases, patients may experience persistent pain. This could be due to complications such as infection or nerve damage. It is important for patients to follow post-operative care instructions. This can help to minimize the risk of complications.
See also: Can Hair Transplant Scars Be Removed?
Managing Post-Operative Pain
Pain Medication
Pain medication is commonly prescribed after a hair transplant. This can include over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. In some cases, stronger prescription pain medication may be needed. It is important for patients to take medication as directed by their surgeon.
Post-Operative Care Instructions
Following post-operative care instructions is crucial. This can help to minimize pain and ensure proper healing. Instructions may include keeping the scalp clean, avoiding strenuous activity, and protecting the treated areas from sun exposure. Patients should also avoid scratching or picking at the scalp.
Cold Compresses
Applying cold compresses can help to reduce swelling and discomfort. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions on how to use cold compresses. It is important not to apply ice directly to the scalp.
Sleeping Position
Sleeping with the head elevated can help to reduce swelling and discomfort. Patients may be advised to sleep with several pillows or use a recliner. This can help to minimize pressure on the treated areas.
Factors Influencing Pain Perception
Individual Pain Tolerance
Pain tolerance varies from person to person. Some individuals may have a higher tolerance for pain. Others may be more sensitive. This can influence their perception of pain during and after the procedure.
Extent of the Procedure
The extent of the procedure can also influence pain levels. Larger procedures may result in more discomfort. This is because more areas of the scalp are being treated. Patients undergoing smaller procedures may experience less discomfort.
Surgeon’s Technique
The technique used by the surgeon can also impact pain levels. Experienced surgeons may use methods that minimize discomfort. This can include using smaller instruments or employing specific techniques to reduce trauma to the scalp.
Psychological Factors
Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress can influence pain perception. Patients who are anxious about the procedure may perceive pain more intensely. Managing anxiety through relaxation techniques or sedatives can help.
Expectations
Having realistic expectations is important. Patients who expect the procedure to be painless may be more sensitive to discomfort. Understanding that some discomfort is normal can help patients to better cope with pain.
Communication with the Surgeon
Discussing Pain Concerns
Patients should discuss any pain concerns with their surgeon. This can include discussing pain tolerance, anxiety, and previous experiences with pain. Open communication can help the surgeon to develop a pain management plan tailored to the patient’s needs.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are important. They allow the surgeon to monitor the patient’s healing. They also provide an opportunity to address any pain concerns. Patients should not hesitate to discuss any discomfort they are experiencing during follow-up visits.
Conclusion
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves some level of discomfort. The use of local anesthesia ensures that the procedure itself is not painful. However, patients may experience some discomfort or pain after the procedure. This can be managed with pain medication and proper post-operative care. Individual pain tolerance, the extent of the procedure, and the surgeon’s technique can all influence pain levels. Open communication with the surgeon is important for effective pain management. By understanding the potential for discomfort and following post-operative care instructions, patients can achieve successful results with minimal pain.
You May Be Interested In