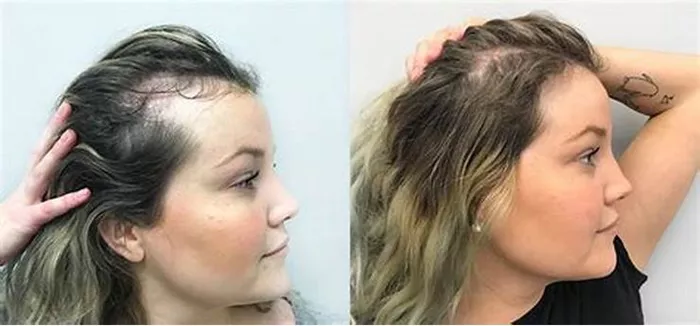
Hair transplantation is a popular solution for those experiencing hair loss. However, there are concerns about the longevity of transplanted hair. One common question is whether transplanted hair can fall out after two years. This article explores this topic in detail.
Understanding Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation involves moving hair follicles from a donor site (usually the back of the head) to a recipient site (the balding area). The two primary methods are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT involves removing a strip of scalp and dissecting it into individual grafts, while FUE involves extracting individual follicles directly from the scalp.
The Hair Growth Cycle
Hair growth occurs in cycles: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). After a hair transplant, the new hair follows the same cycle.
Initial Shedding:
Transplanted hair typically sheds 2-3 weeks post-surgery.
This is a normal part of the process called “shock loss.”
New hair growth usually begins 3-4 months later.
Growth and Maturation:
Hair continues to grow and thicken over the first year.
By 12-18 months, the full results are typically visible.
Why Transplanted Hair Might Fall Out After Two Years
While hair transplantation is generally successful, some patients experience hair loss even after two years. Several factors can contribute to this:
1. Genetic Predisposition
Androgenetic Alopecia: If you have a genetic predisposition to hair loss, non-transplanted hair may continue to thin and fall out.
Donor Area Quality: The success of a transplant largely depends on the quality of the donor area. If the donor hair is prone to thinning, it may affect the longevity of the transplanted hair.
2. Improper Post-Operative Care
Neglecting Post-Surgery Instructions: Failure to follow post-operative care instructions can lead to complications, affecting the survival of transplanted hair.
Infections: Poor hygiene can result in infections that damage hair follicles.
3. Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Physical and Emotional Stress: Stress can trigger hair loss, even in transplanted hair.
Poor Diet and Lifestyle Choices: Lack of essential nutrients and unhealthy habits can affect hair health.
4. Medical Conditions
Scalp Conditions: Conditions like dermatitis or psoriasis can affect hair growth.
Hormonal Imbalances: Thyroid disorders or other hormonal issues can contribute to hair loss.
5. Aging
Natural Hair Cycle: Hair naturally thins with age. Even transplanted hair can be subject to the effects of aging.
See also: Can You Drink Coffee After a Hair Transplant?
Preventing Transplanted Hair Loss
While some factors are beyond control, there are steps you can take to maintain transplanted hair.
1. Follow Post-Operative Instructions
Adhere strictly to your surgeon’s instructions regarding hair care post-surgery.
Avoid activities that can harm the transplanted area, such as heavy exercise or direct sunlight exposure, in the initial weeks.
2. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Balanced Diet: Ensure your diet is rich in vitamins and minerals essential for hair health, such as biotin, zinc, and iron.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your scalp hydrated.
Regular Exercise: Exercise improves blood circulation, promoting healthy hair growth.
3. Manage Stress
Practice stress-relief techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Ensure you get enough sleep to support overall health.
4. Regular Check-Ups
Visit your dermatologist regularly to monitor the health of your scalp and hair.
Address any medical conditions that may affect hair growth promptly.
5. Hair Care Routine
Use mild shampoos and conditioners that are free from harsh chemicals.
Avoid excessive heat styling, which can damage hair.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice significant hair loss after two years of a hair transplant, it is essential to consult your surgeon or a dermatologist. They can determine the cause and suggest appropriate treatments.
Possible Treatments
Medications: Minoxidil and finasteride are commonly prescribed to support hair growth.
PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma therapy can stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
Additional Transplants: In some cases, another transplant may be necessary.
Conclusion
While it is uncommon for transplanted hair to fall out after two years, it is not impossible. Factors such as genetic predisposition, lifestyle, medical conditions, and aging can affect the longevity of transplanted hair. By following post-operative care instructions, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking regular medical advice, you can maximize the success of your hair transplant and enjoy long-lasting results. If you experience significant hair loss after a transplant, consult your doctor to explore potential treatments and solutions.
FAQs
Why is my hair transplant falling out after 2 years?
Hair transplant falling out after 2 years can occur due to several reasons:
Genetic Predisposition: If you have a genetic tendency for hair loss, transplanted hair may not be immune and could thin over time.
Poor Maintenance: Inadequate post-operative care or failure to follow instructions can affect the survival of transplanted hair.
Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like scalp infections or autoimmune disorders can impact hair follicles.
Natural Hair Cycle: Like natural hair, transplanted hair goes through growth cycles, and shedding can occur as part of this process.
How many years does a hair transplant last?
The longevity of a hair transplant varies:
Permanent Hair: Typically, transplanted hair is considered permanent because it is taken from donor areas genetically resistant to balding.
Initial Shedding: It’s normal for transplanted hair to shed initially, usually within the first few weeks.
Long-term Results: With proper care and maintenance, transplanted hair can last a lifetime. However, individual factors like genetics, lifestyle, and health can influence longevity.
Will transplanted hair fall out again?
Transplanted hair can fall out again under certain circumstances:
Genetic Factors: If you have ongoing genetic hair loss, surrounding non-transplanted hair may continue to thin.
Poor Maintenance: Neglecting post-operative care instructions can affect the survival of transplanted hair.
Underlying Health Issues: Conditions affecting hair follicles or systemic health can impact transplanted hair.
Aging Process: Natural aging can affect all hair, including transplanted follicles.
You May Be Interested In