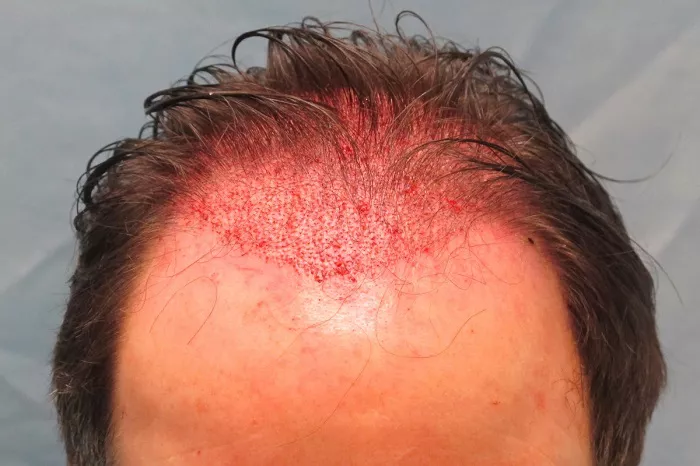
Hair transplantation is a complex surgical procedure that aims to restore hair growth in areas affected by baldness or thinning. While it is generally a well-controlled process, some patients may experience bleeding even after the procedure, which can cause concern. Understanding the reasons behind this bleeding is crucial for both patients and medical professionals involved in the hair transplant field.
The Normal Course of Bleeding During and After Hair Transplant
During the Procedure:
Hair transplantation involves making incisions in the scalp to implant hair follicles. These incisions, whether they are made using the follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE) method, will naturally lead to some bleeding. During the surgery, the medical team takes measures to control this bleeding. They may use local anesthesia, which has vasoconstrictive properties to reduce blood flow, and apply direct pressure or use electrocautery to stop the bleeding from the opened blood vessels. However, it is impossible to completely eliminate all bleeding during the operation as the scalp is a highly vascular area.
Immediate Post-Procedure:
In the hours immediately following the hair transplant, it is normal to have some oozing of blood. This is usually a slow and minimal amount of bleeding that can be managed with the dressings and instructions provided by the medical staff. The body’s natural clotting mechanisms start to work, and the bleeding should gradually subside. For example, a small amount of blood may seep through the gauze placed on the scalp, but this is not a cause for major alarm as long as it is not excessive.
Reasons for Persistent Bleeding After Hair Transplant
High Blood Pressure:
One of the main factors that can lead to continued bleeding is high blood pressure. When a patient has elevated blood pressure, the force of the blood against the walls of the blood vessels is increased. This can cause the blood vessels that were damaged during the hair transplant to continue to bleed or reopen. Even if the bleeding was initially controlled during the surgery, the persistent high pressure can disrupt the clotting process. Patients with pre-existing hypertension or those who experience a spike in blood pressure after the procedure due to stress or other factors are more likely to have this issue.For instance, if a patient gets excited or stressed about the procedure and their blood pressure rises, it can lead to renewed bleeding from the scalp.
Medications and Supplements:
Certain medications and supplements can affect the blood’s ability to clot. Anticoagulants such as aspirin, warfarin, or some herbal supplements like ginkgo biloba and fish oil can thin the blood. If a patient is taking these substances and did not disclose this information to the hair transplant surgeon prior to the procedure, it can increase the risk of bleeding. The surgeon may have adjusted the surgical approach or asked the patient to stop taking these medications temporarily if they had known. But in cases where this information was withheld, it can lead to unexpected and prolonged bleeding.
Excessive Physical Activity:
Engaging in strenuous physical activity too soon after a hair transplant can cause bleeding. Activities that increase blood flow to the head, such as heavy lifting, bending over frequently, or intense exercise, can put pressure on the newly implanted follicles and the healing incisions. This can disrupt the clotting that has taken place and cause the blood vessels to start bleeding again. For example, a patient who goes to the gym and starts lifting weights a day or two after the transplant is likely to experience bleeding from the scalp.
Poor Wound Healing:
Some patients may have underlying conditions that affect wound healing. Diabetes, for instance, can impair the body’s ability to repair damaged tissues and form proper blood clots. If a patient has diabetes and their blood sugar levels are not well-controlled, it can lead to slower healing and increased bleeding. Additionally, nutritional deficiencies, such as a lack of vitamin C or zinc, which are essential for collagen synthesis and wound repair, can also contribute to poor wound healing and persistent bleeding.
Prevention and Management of Post-Hair Transplant Bleeding
Pre-Procedure Precautions:
Medical History Disclosure: It is of utmost importance for patients to provide a detailed medical history to their hair transplant surgeon. This includes information about any pre-existing medical conditions, medications they are taking, and supplements they use. The surgeon can then make an informed decision about whether any adjustments need to be made to the patient’s treatment plan prior to the surgery.
Blood Pressure Control: If a patient has a history of high blood pressure, the doctor may recommend measures to control it before the procedure. This could involve adjusting medications or lifestyle changes such as reducing salt intake, increasing physical activity (but not immediately before the transplant), and managing stress.
Post-Procedure Care:
Rest and Avoidance of Strenuous Activity: Patients should be instructed to rest as much as possible in the days following the hair transplant. They should avoid any activities that could increase blood flow to the head, such as bending over, heavy lifting, or vigorous exercise. This allows the body’s natural healing mechanisms to work without disruption.
Wound Care: Following the doctor’s instructions for wound care is essential. This may include keeping the scalp clean using a mild shampoo recommended by the surgeon, gently patting the scalp dry instead of rubbing, and changing dressings as directed. Proper wound care helps to prevent infection, which can also affect bleeding and healing.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are necessary. The doctor can monitor the healing progress and check for any signs of bleeding or other complications. If bleeding occurs, the doctor can take appropriate measures such as applying additional pressure, using topical hemostatic agents, or adjusting medications if needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while some bleeding is normal during and immediately after a hair transplant, persistent bleeding can be a cause for concern. Understanding the various factors that can contribute to this bleeding, such as high blood pressure, medications, physical activity, and poor wound healing, is essential for both patients and surgeons. By taking appropriate pre-procedure precautions and following post-procedure care guidelines, the risk of excessive bleeding can be minimized, and the chances of a successful hair transplant outcome can be maximized. Patients should always communicate openly with their surgeons and follow their advice to ensure a smooth recovery process.