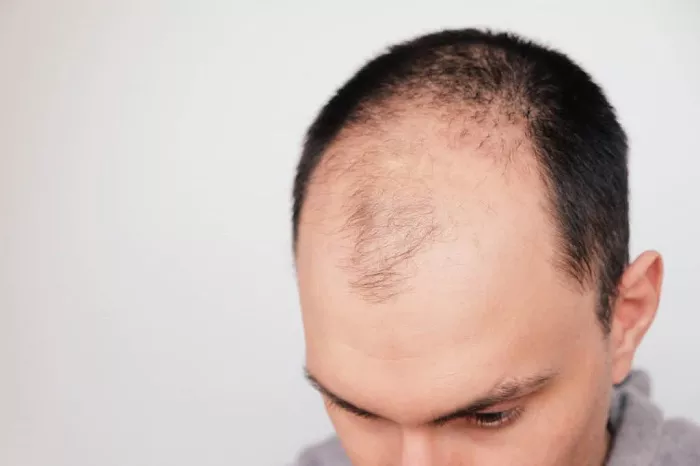
Hair fall at an early age can be a cause of great concern and can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and confidence. While it is normal to lose some hair daily as part of the hair growth cycle, excessive hair fall in one’s teens, twenties, or early thirties is not typical and often indicates an underlying issue. Understanding the various reasons behind this premature hair fall is crucial in order to address the problem effectively and take appropriate preventive or corrective measures.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in determining hair characteristics and susceptibility to hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia:
This is the most common form of genetic hair loss. It is often referred to as male pattern baldness in men and female pattern baldness in women, although the pattern and severity can vary. In men, it usually starts with a receding hairline at the temples and thinning at the crown. In women, it typically involves a general thinning of the hair over the top of the scalp. The genes inherited from parents can predispose an individual to this condition, which is triggered by the action of hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT binds to hair follicles and gradually causes them to shrink and produce thinner, shorter hairs until they eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Family History:
If there is a history of hair loss in the family, especially among close relatives like parents or grandparents, the likelihood of experiencing premature hair fall due to genetic factors is increased. Even if the specific pattern of hair loss is not identical, the genetic predisposition can still manifest in different ways, such as earlier onset or more rapid progression of hair thinning.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes can have a profound impact on hair growth and lead to excessive hair fall.
Thyroid Disorders:
An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. In hyperthyroidism, the body’s metabolism is sped up, which can cause hair to become brittle and break easily.
Hypothyroidism, on the other hand, slows down metabolism and can lead to dry, coarse hair and increased hair shedding.Symptoms of thyroid disorders may include fatigue, weight changes, and changes in heart rate, in addition to the hair-related issues.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
This is a common hormonal disorder in women that is characterized by an imbalance of androgens (male hormones) in the body. The increased levels of androgens can lead to a variety of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and hair loss. The hair loss in PCOS often resembles male pattern baldness, with thinning at the temples and crown. Women with PCOS may also experience excessive hair growth in other areas, such as the face and body, due to the hormonal imbalance.
Puberty and Menstrual Cycle Changes:
During puberty, hormonal fluctuations can sometimes cause temporary hair loss. The body is adjusting to new hormonal levels, and this can affect the hair growth cycle. Similarly, changes in hormone levels during the menstrual cycle can also lead to increased hair shedding in some women. This is usually a mild and transient phenomenon, but for some, it can be more noticeable and cause concern.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A diet lacking in essential nutrients can have a negative impact on hair health.
Protein Deficiency:
Hair is made up mostly of a protein called keratin. If the diet does not provide enough protein, the body may not be able to produce healthy hair. This can lead to weak, brittle hair that breaks easily and falls out. Good sources of protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, and nuts. Vegetarians and vegans need to be especially careful to ensure they are getting an adequate supply of plant-based proteins.
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies:
B Vitamins: Biotin, in particular, is important for hair health. A deficiency in biotin can cause hair to become thin and brittle and may lead to increased hair fall. Other B vitamins, such as niacin, pantothenic acid, and folic acid, also play a role in maintaining healthy hair. Foods rich in B vitamins include whole grains, leafy greens, and fortified cereals.
Vitamin D: This vitamin is essential for calcium absorption and also has a role in hair follicle health. A lack of vitamin D can lead to hair loss, as well as other health issues. Sun exposure is a natural source of vitamin D, but it can also be obtained from fortified foods and supplements.
Iron: Iron deficiency anemia is a common cause of hair loss, especially in women. Iron is needed for the production of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to the cells, including the hair follicles. Without enough iron, the follicles may not receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients, leading to hair thinning and shedding. Red meat, spinach, and lentils are good sources of iron.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Modern lifestyles can contribute to premature hair fall.
Chronic Stress:
High levels of stress can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. Stress triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol, which can cause hair follicles to enter a resting phase prematurely. This leads to increased hair shedding. Examples of stressors include work pressure, academic stress, relationship problems, and financial difficulties. Prolonged stress can have a cumulative effect on hair health and may result in significant hair loss over time.
Poor Sleep Habits:
Lack of sleep or poor quality sleep can also affect hair growth. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates, and this includes the hair follicles. If a person consistently gets less than the recommended 7 – 8 hours of sleep per night, it can disrupt the hormonal balance and the body’s natural repair processes, leading to hair thinning and loss.
Unhealthy Diet and Excessive Smoking or Alcohol Consumption:
A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and fats can contribute to nutritional deficiencies and inflammation in the body, which can affect hair health. Additionally, smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the scalp and depriving the hair follicles of oxygen and nutrients. Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt liver function and affect hormone metabolism, both of which can lead to hair loss.
Conclusion
Premature hair fall can have multiple causes, often involving a combination of genetic, hormonal, nutritional, stress, and lifestyle factors. Identifying the specific reason or reasons behind the hair loss is the first step in addressing the issue. This may require a visit to a doctor or a dermatologist, who can conduct a thorough examination, order relevant tests, and provide a proper diagnosis. Once the cause is determined, appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes can be implemented. These may include dietary adjustments, hormone therapy in some cases, stress management techniques, and the use of hair care products designed to promote hair health.