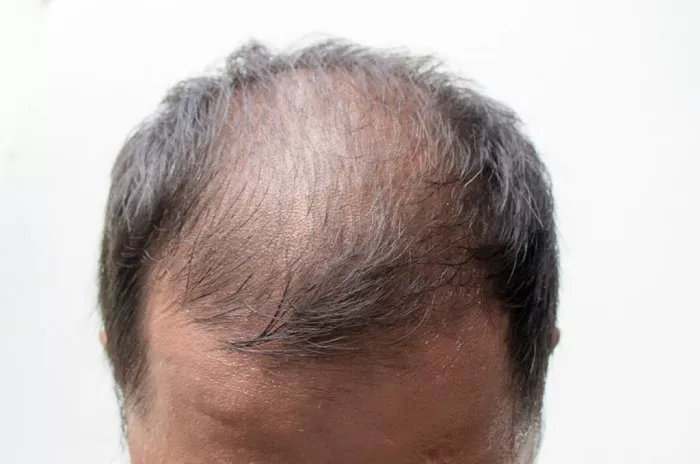
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness, is a common form of hair loss that affects both men and women. This condition is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors and can result in thinning hair and baldness. In this article, we will explore whether hair can grow back with androgenetic alopecia and the available treatments for this condition.
What is Androgenetic Alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness, is a common form of hair loss that affects both men and women. It is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors and can result in thinning hair and baldness. Androgenetic alopecia is more common in men, but it can also affect women. It is characterized by a progressive loss of hair from the scalp, typically starting with the hairline in men and the crown of the head in women. The condition is inherited from one or both parents and can be triggered by hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. While hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia is permanent, there are treatments available that can help to slow down or stop the progression of hair loss and even regrow hair in some cases. Patients should consult with a hair loss specialist to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs and hair type.
Causes of Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. Here are some detailed explanations of the causes of androgenetic alopecia:
Genetic Factors:
Androgenetic alopecia is an inherited condition that is passed down from one or both parents. The condition is caused by a genetic predisposition to sensitivity to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is produced from testosterone in the scalp. DHT causes the hair follicles to shrink and eventually stop producing hair.
Hormonal Factors:
Hormonal changes can also trigger androgenetic alopecia. DHT is produced from testosterone in the scalp, and hormonal changes that increase the production of testosterone can lead to increased levels of DHT and hair loss. Hormonal changes that can trigger androgenetic alopecia include puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Age:
Androgenetic alopecia is more common in older adults, as the hair follicles become more sensitive to DHT with age. This can lead to a progressive loss of hair from the scalp over time.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can also contribute to androgenetic alopecia. These conditions include thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and scalp infections. Medications used to treat these conditions can also contribute to hair loss.
Lifestyle Factors:
Lifestyle factors such as stress, poor nutrition, and smoking can also contribute to androgenetic alopecia. Stress can increase the production of hormones that contribute to hair loss, while poor nutrition can lead to vitamin and mineral deficiencies that can affect hair growth. Smoking can also contribute to hair loss by reducing blood flow to the scalp.
In conclusion, androgenetic alopecia is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, as well as age, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. While the condition is inherited from one or both parents, hormonal changes and other factors can trigger and contribute to hair loss. By understanding the causes of androgenetic alopecia, patients can take steps to prevent or slow down hair loss and seek appropriate treatment to improve hair growth and appearance.
Symptoms of Androgenetic Alopecia
The symptoms of androgenetic alopecia can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms of androgenetic alopecia:
Thinning Hair:
The most common symptom of androgenetic alopecia is thinning hair on the crown and front of the scalp. This can lead to a visible reduction in hair density and overall volume.
Receding Hairline:
In men, androgenetic alopecia can cause a receding hairline, which is the gradual loss of hair at the front of the scalp. This can result in a “M” shaped pattern of hair loss.
Widening Part:
In women, androgenetic alopecia can cause a widening part, which is the gradual loss of hair along the part line on the top of the scalp.
Bald Spots:
In severe cases, androgenetic alopecia can cause bald spots on the scalp. These bald spots may be small and circular or larger and irregularly shaped.
Miniaturized Hair:
Hair affected by androgenetic alopecia may become thinner and shorter over time. This is known as miniaturization and is caused by the shrinking of hair follicles.
Itching or Burning Sensation:
Some individuals with androgenetic alopecia may experience itching or burning sensations on the scalp.
Excessive Hair Shedding:
Individuals with androgenetic alopecia may experience excessive shedding of hair, particularly during washing or brushing.
It is important to note that the symptoms of androgenetic alopecia can vary from person to person and may progress at different rates. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a hair loss specialist to determine the cause of your hair loss and develop an appropriate treatment plan. By seeking early treatment, individuals with androgenetic alopecia can slow down or even reverse the progression of hair loss and improve hair growth and appearance.
Can Hair Grow Back with Androgenetic Alopecia?
Hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia is permanent, and the hair will not grow back on its own. However, there are treatments available that can help to slow down or stop the progression of hair loss and even regrow hair in some cases.
Minoxidil is a topical medication that is applied to the scalp to stimulate hair growth. It is available over-the-counter and can be used by both men and women. Finasteride is an oral medication that is used to treat hair loss in men. It works by blocking the production of a hormone called DHT, which is responsible for hair loss.
Hair transplant surgery involves removing hair follicles from one part of the scalp and transplanting them to another part of the scalp. This procedure can be effective in restoring hair growth in areas of the scalp that have experienced hair loss.
Low-level laser therapy involves using a device that emits low-level laser light to stimulate hair growth. This treatment can be used by both men and women and is available in clinics and for home use.
Available Treatments for Androgenetic Alopecia
There are several treatments available for androgenetic alopecia, including:
Minoxidil:
Minoxidil is a topical medication that is applied to the scalp to stimulate hair growth. It is available over-the-counter and can be used by both men and women. Minoxidil works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles and prolonging the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle. It may take several months to see results, and the medication must be used continuously to maintain hair growth.
Finasteride:
Finasteride is an oral medication that is used to treat hair loss in men. It works by blocking the production of a hormone called DHT, which is responsible for hair loss. Finasteride is only available by prescription and must be taken daily to maintain hair growth. It may take several months to see results, and the medication may cause side effects such as decreased libido and erectile dysfunction.
Hair Transplant Surgery:
Hair transplant surgery involves removing hair follicles from one part of the scalp and transplanting them to another part of the scalp. This procedure can be effective in restoring hair growth in areas of the scalp that have experienced hair loss. Hair transplant surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia and may require multiple sessions to achieve desired results. The procedure may cause temporary swelling and scabbing, and patients must follow proper aftercare instructions to ensure proper healing.
Low-Level Laser Therapy:
Low-level laser therapy involves using a device that emits low-level laser light to stimulate hair growth. This treatment can be used by both men and women and is available in clinics and for home use. Low-level laser therapy works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles and prolonging the anagen phase of the hair cycle. It may take several months to see results, and the treatment must be used continuously to maintain hair growth.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of platelets and growth factors into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood and is believed to promote healing and tissue regeneration. PRP therapy may require multiple sessions to achieve desired results, and the treatment may cause temporary swelling and discomfort.
Scalp Micropigmentation:
Scalp micropigmentation involves tattooing the scalp with small dots to create the appearance of hair follicles. This treatment is typically used to create the appearance of a closely shaved head and may be used in conjunction with other hair loss treatments.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of these treatments can vary from person to person, and results may take several months to become visible. Patients should consult with a hair loss specialist to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs and hair type. By following proper hair care and maintenance, patients with androgenetic alopecia can enjoy improved hair growth and appearance.
Conclusion
Androgenetic alopecia is a common form of hair loss that is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. While hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia is permanent, there are treatments available that can help to slow down or stop the progression of hair loss and even regrow hair in some cases. Patients should consult with a hair loss specialist to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs and hair type. With proper treatment and care, patients with androgenetic alopecia can enjoy improved hair growth and appearance.
Related Topics: