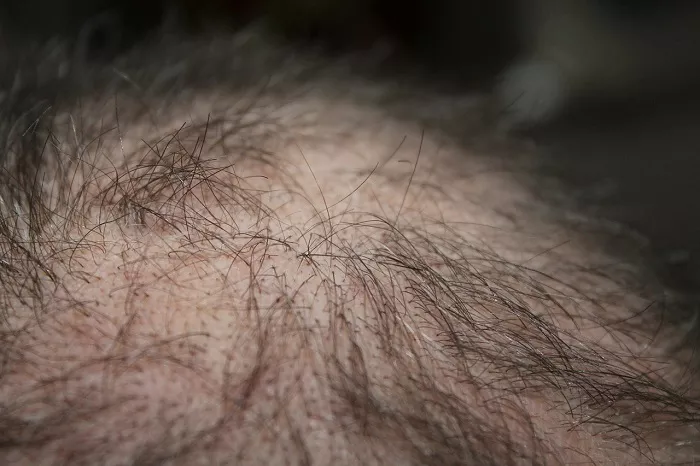
Thinning hair is a common problem that affects many people, both men and women. Thinning hair can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, aging, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. In this article, we will discuss what thinning hair looks like and what you can do to treat it.
What is Thinning Hair?
Thinning hair refers to a reduction in the density and volume of hair. It occurs when hair strands become finer and shorter, and hair follicles produce fewer hair strands. Thinning hair can occur gradually over time or suddenly. Thinning hair can affect any area of the scalp, but it is most commonly seen in the crown area and the hairline.
Thinning hair is a common problem that affects many people, both men and women. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, aging, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Hereditary hair loss is a common cause of thinning hair, and it is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. As we age, our hair follicles shrink and produce thinner hair strands, leading to hair thinning. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders, can affect hair growth and lead to hair thinning. Certain medical conditions, such as alopecia areata and trichotillomania, can also cause hair thinning.
Signs of Thinning Hair
There are several signs of thinning hair that you can look out for. These include:
A widening part:
If your part is becoming wider than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair.
A visible scalp:
If you can see more of your scalp than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair.
Reduced volume:
If your hair feels less full and voluminous than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair.
Hair shedding:
If you are experiencing more hair shedding than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair. Thinning hair is a common problem that affects many people, both men and women. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, aging, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Here are some signs of thinning hair that you can look out for:
A Widening Part:
If your part is becoming wider than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair. This is especially true for people who have a middle part.
Visible Scalp:
If you can see more of your scalp than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair. This can be especially noticeable at the crown of the head.
Reduced Volume:
If your hair feels less full and voluminous than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair. This can be especially noticeable when styling your hair.
Hair Shedding:
If you are experiencing more hair shedding than usual, it may be a sign of thinning hair. This can be especially noticeable when brushing or washing your hair.
Thinning Hairline:
If you notice that your hairline is receding, it may be a sign of thinning hair. This is especially true for men, who commonly experience a receding hairline.
If you are experiencing any of these signs, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of your thinning hair and the best treatment options for your specific case. Early intervention is key in preventing further hair loss and promoting healthy hair growth.
Causes of Thinning Hair
There are several causes of thinning hair, including:
Genetics:
Hereditary hair loss is a common cause of thinning hair. This type of hair loss is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors and can lead to gradual hair thinning and baldness.
Aging:
As we age, our hair follicles shrink and produce thinner hair strands, leading to hair thinning.
Hormonal changes:
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders, can affect hair growth and lead to hair thinning.
Medical conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as alopecia areata and trichotillomania, can cause hair thinning.
Treatment Options:
There are several treatment options available for thinning hair, including:
Medications:
Finasteride and minoxidil are two FDA-approved medications that are commonly used to treat thinning hair. Finasteride works by blocking the production of DHT, while minoxidil works by stimulating hair follicles and promoting hair growth.
Hair Transplant:
Hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves taking hair follicles from one part of the scalp and transplanting them to the thinning area. This procedure is effective for treating thinning hair and can provide long-lasting results.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of platelets into the scalp to promote hair growth. Platelets contain growth factors that stimulate hair growth and improve the health of hair follicles.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
LLLT involves using a laser device to stimulate hair growth. The laser light penetrates the scalp and stimulates hair follicles, promoting hair growth.
Lifestyle Changes:
Making lifestyle changes can also help to prevent and treat thinning hair. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals can help to promote healthy hair growth. Avoiding tight hairstyles, such as tight braids or ponytails, and avoiding heat styling can also help to prevent further hair damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thinning hair is a common problem that can be caused by a variety of factors. Signs of thinning hair include a widening part, visible scalp, reduced volume, and hair shedding. Treatment options for thinning hair include medications, hair transplant, PRP therapy, LLLT, and lifestyle changes. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment options for your specific case. Early intervention is key in preventing further hair loss and promoting healthy hair growth.
Related Topics: