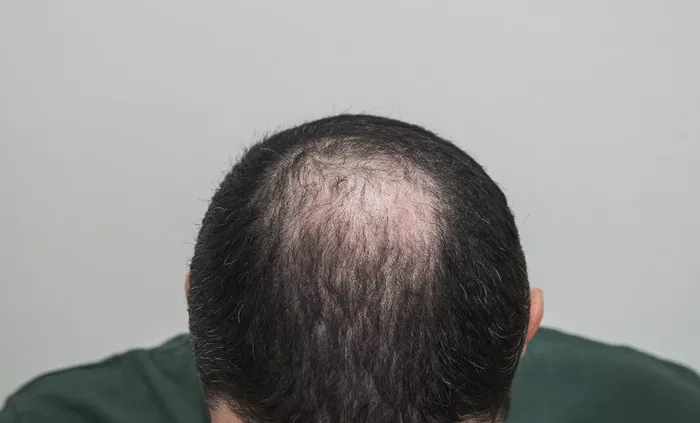
Androgenic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness, is one of the most common causes of hair loss in both men and women. This hereditary condition is characterized by a gradual thinning of the hair, leading to partial or complete baldness over time. While androgenic alopecia is often seen as a natural part of aging, many individuals seek effective treatments to slow down the process and, in some cases, reverse the effects.
This article will explore proven methods for managing androgenic alopecia, focusing on treatments that can help stimulate hair growth and improve the overall health of the scalp. Understanding how these treatments work is key to making informed decisions on how to address hair loss.
What is Androgenic Alopecia?
Androgenic alopecia is a genetic condition that leads to hair loss, usually in a predictable pattern. It occurs due to a combination of hormones and genetic predisposition. The main hormone involved is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT affects the hair follicles, causing them to shrink, weaken, and eventually stop producing hair.
In men, androgenic alopecia typically presents as a receding hairline or thinning at the crown, eventually leading to baldness on the top of the head. In women, the hair loss is usually more diffuse, causing overall thinning but rarely leading to complete baldness.
Causes of Androgenic Alopecia
The primary cause of androgenic alopecia is genetic inheritance. If one or both parents experienced pattern baldness, there is a higher likelihood that their offspring will also experience hair loss. Hormonal changes, specifically the overproduction of DHT, play a significant role in the progression of this condition. DHT binds to the receptors in hair follicles, shortening the hair’s growth cycle and reducing the size of the follicles.
Other factors that can contribute to or exacerbate androgenic alopecia include:
Age: The likelihood of developing androgenic alopecia increases with age.
SEE ALSO: What Age Do Guys Start Losing Hair
Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones, especially after pregnancy or during menopause, can trigger hair loss in women.
Stress: Chronic stress may accelerate hair thinning by disrupting the normal hair growth cycle.
Nutritional deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin D can weaken hair, making it more susceptible to shedding.
Medications That Help Androgenic Alopecia
There are several FDA-approved medications that can help slow the progression of androgenic alopecia and, in some cases, promote regrowth.
Minoxidil (Topical Treatment)
Minoxidil is one of the most common treatments for androgenic alopecia. It is an over-the-counter medication available in foam or liquid form, applied directly to the scalp. Minoxidil works by prolonging the growth phase of the hair cycle and improving blood flow to the hair follicles, helping to prevent further hair loss and, in some cases, stimulate regrowth.
Minoxidil is most effective for individuals experiencing early stages of hair loss. Consistent use is necessary to maintain results, and discontinuation of the treatment will likely result in a return to hair loss.
Finasteride (Oral Medication)
Finasteride is a prescription medication primarily used for treating male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. By reducing DHT levels in the scalp, finasteride helps slow down hair loss and may promote regrowth.
However, finasteride is generally recommended for men, as it can cause significant side effects in women, especially during pregnancy. Like minoxidil, continuous use is required to maintain the benefits.
Spironolactone (For Women)
Spironolactone is an anti-androgen medication that is sometimes prescribed to women with androgenic alopecia. It blocks the effects of androgens like DHT on hair follicles. While spironolactone is not FDA-approved for treating hair loss, it has been shown to be effective in many women, especially those who experience hormonal imbalances or are undergoing menopause.
Non-Medication Treatments for Androgenic Alopecia
While medications are a key approach to managing androgenic alopecia, there are several non-drug options that can also help slow down hair loss and improve the health of the scalp.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that uses red light to stimulate hair follicles and encourage growth. The light is absorbed by the cells in the scalp, which increases blood flow and supports follicle health.
LLLT is most effective when used in the early stages of androgenic alopecia. It can be used alone or in conjunction with other treatments like minoxidil or finasteride. Many at-home devices, such as laser combs or caps, are available for convenient use.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves drawing a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma back into the scalp. The growth factors in the plasma help to stimulate hair follicles and encourage regrowth.
This therapy is particularly promising for individuals with early-stage androgenic alopecia, as it may help strengthen existing follicles and slow down the hair loss process. PRP treatments typically require multiple sessions, with results appearing gradually over several months.
Hair Transplant Surgery
For those with more advanced androgenic alopecia, hair transplant surgery may be a viable option. Hair transplants involve harvesting hair from a donor area of the scalp (usually the back or sides) and transplanting it to areas experiencing thinning or baldness.
There are two main types of hair transplant procedures:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of scalp with healthy hair follicles is removed, and the follicles are transplanted to balding areas.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual hair follicles are extracted and transplanted, which leaves less scarring and offers a faster recovery time.
Hair transplant surgery provides permanent results, though it can be costly and requires a skilled surgeon for optimal outcomes.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes That Help Androgenic Alopecia
Though genetics and hormones largely drive androgenic alopecia, lifestyle changes can support overall hair health and potentially slow down the progression of hair loss.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet
A nutrient-rich diet is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Key nutrients that support hair health include:
Protein: Hair is made of keratin, a type of protein, so it is important to consume enough protein to support hair growth.
Iron: Iron deficiency can lead to hair thinning, so it’s important to include iron-rich foods like spinach, lentils, and lean meats.
Zinc: Zinc helps maintain the oil glands around hair follicles, promoting healthy hair.
Vitamins D and E: Vitamin D supports the hair cycle, while vitamin E protects the scalp from oxidative stress.
Reducing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can worsen hair loss by disrupting the hair growth cycle. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or regular physical activity can improve scalp health and slow the progression of androgenic alopecia.
Proper Hair Care Practices
Gentle hair care practices can help prevent unnecessary damage to thinning hair. Avoiding excessive heat styling, chemical treatments, and harsh hair products can minimize breakage and promote stronger hair growth. It’s also beneficial to use shampoos and conditioners that are specifically formulated to strengthen hair and support scalp health.
Conclusion
Androgenic alopecia is a common form of hair loss, but there are several effective treatments that can help slow its progression and, in some cases, promote regrowth. Medications like minoxidil, finasteride, and spironolactone are widely used to manage hair loss, while non-medication treatments such as LLLT, PRP therapy, and hair transplant surgery offer additional options. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and stress management, can support overall hair health and slow down the effects of androgenic alopecia.
If you are experiencing hair loss, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation. With the right combination of treatments, you can manage androgenic alopecia and maintain a healthy scalp for years to come.
You Might Be Interested In