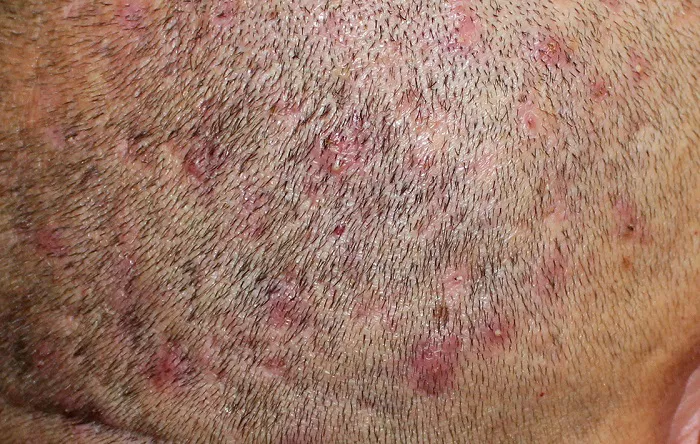
Hair transplantation has become a common and effective solution for many people dealing with hair loss. However, like any surgical procedure, it can come with a range of post – operative experiences. One of the concerns that patients often have is whether it is normal to feel sick after a hair transplant. Understanding the various aspects related to this question is crucial for patients to know what to expect and when to seek medical attention.
The Surgical Process and Its Impact
Anesthesia Effects
During a hair transplant, local or sometimes regional anesthesia is usually used. The anesthesia can have lingering effects after the procedure. Some patients may experience mild nausea, dizziness, or a general feeling of being unwell as a result of the anesthesia wearing off. This is because the body is adjusting to the chemicals that were introduced to numb the area during the surgery. For example, local anesthetics can sometimes affect the normal functioning of the nervous system in the short term, leading to these discomforts. However, these symptoms are usually temporary and should subside within a few hours to a day as the body metabolizes the anesthesia.
Physical Trauma from the Procedure
A hair transplant involves making incisions in the scalp, whether it’s for the removal of a strip of tissue in follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or the extraction of individual follicles in follicular unit extraction (FUE). This physical trauma can cause the body to respond in various ways. The body’s immune system kicks in to start the healing process, and this can sometimes lead to a feeling of malaise. There may be a slight elevation in body temperature as the body is dealing with the inflammation caused by the surgical wounds. Additionally, the pain and discomfort from the procedure itself can contribute to an overall sense of sickness. The scalp is a very sensitive area, and the sensations from the healing wounds can affect the patient’s well – being.
Post – Operative Medications and Their Side Effects
Painkillers and Antibiotics
After a hair transplant, patients are often prescribed painkillers to manage any discomfort and antibiotics to prevent infection. These medications can have side effects that might make the patient feel sick. For instance, some common painkillers can cause stomach upset, including nausea, vomiting, or indigestion. This is because they may irritate the lining of the stomach. Antibiotics can also have similar effects. They can disrupt the normal balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to gastrointestinal issues. Moreover, some patients may be allergic to certain types of antibiotics, which can cause more severe symptoms such as severe nausea, rashes, or difficulty breathing. It is important for patients to inform their doctors of any known allergies before starting these medications.
Anti – Inflammatory Drugs
Anti – inflammatory drugs are sometimes prescribed to reduce the swelling and inflammation in the scalp after the transplant. These drugs can also have side effects that contribute to a feeling of sickness. They may affect the kidneys or liver in some cases, although this is relatively rare. More commonly, they can cause mild gastrointestinal problems or headaches. The body’s reaction to these drugs varies from person to person, and some patients may be more sensitive to their effects than others.
Psychological Factors and Their Influence
Stress and Anxiety
Undergoing a hair transplant can be a stressful experience for many patients. The anticipation of the results, concerns about the procedure itself, and the financial investment can all contribute to high levels of stress and anxiety. These psychological factors can manifest physically and make the patient feel sick. Stress can affect the digestive system, causing symptoms like nausea, loss of appetite, or an upset stomach. Additionally, anxiety can lead to a feeling of light – headedness or general unease. It is important for patients to address these psychological aspects either through self – care techniques like relaxation exercises or by seeking professional help if the stress and anxiety become overwhelming.
Body Image Concerns
Even after the procedure, patients may worry about the appearance of their scalp during the healing process. The initial redness, swelling, and the presence of scabs can be a cause for concern. This preoccupation with body image can add to the psychological burden and potentially make the patient feel more unwell. The mind – body connection is strong, and negative thoughts about the appearance can trigger physical symptoms that mimic or exacerbate any existing feelings of sickness.
When to Be Concerned
Severe or Prolonged Symptoms
If the feeling of sickness persists for more than a few days or if it becomes severe, it is a cause for concern. For example, if the nausea is accompanied by persistent vomiting, severe abdominal pain, or high – fever that doesn’t subside, it could indicate an infection or a more serious reaction to the procedure or medications. Similarly, if dizziness or light – headedness is so severe that it affects the patient’s ability to function or is accompanied by fainting, medical attention should be sought immediately.
Signs of Infection
Infection is a potential complication after a hair transplant. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, and pain around the surgical site. Pus or a foul – smelling discharge from the scalp is also a clear indication of infection. If the patient experiences these symptoms along with feeling sick, it is crucial to contact the doctor right away. Early detection and treatment of an infection can prevent more serious complications and ensure the success of the hair transplant.
Conclusion
Feeling sick after a hair transplant can be normal in many cases, especially in the immediate aftermath of the procedure due to factors such as anesthesia, physical trauma, medications, and psychological stress. However, it is important for patients to be aware of the normal range of post – operative symptoms and to know when to be concerned. By closely monitoring their condition, following the doctor’s instructions regarding medications and post – operative care, and communicating any unusual or severe symptoms to the medical team, patients can ensure a smoother recovery process and the best possible outcome for their hair transplant.
Related Topics: